Introduction to PCB Assembly
PCB assembly is a crucial process in the electronics manufacturing industry. It involves soldering or assembling various electrical components, like resistors, capacitors, ICs, connectors, LEDs, etc., onto a PCB to form a functional electronic circuit board. The PCB acts as the structural framework to support and connect the components electrically using copper traces on the board.
Proper PCB assembly requires fabrication, soldering, inspection, and testing expertise to ensure the resulting boards meet quality and reliability standards. It combines manual and automated assembly techniques using surface mount technology (SMT) and robotic machinery. The demand for high-quality PCB assembly services has increased significantly with the growth of advanced electronics across industries like automotive, aerospace, medical, and consumer appliances.
This comprehensive guide provides an in-depth overview of PCB assembly – explaining key terminology and industry standards, choosing an assembly partner, and answering frequently asked questions. Whether you are new to electronics manufacturing or a seasoned production manager, this guide will provide valuable insights into the PCB assembly process. With a clearer understanding of the steps, standards, and options – you can better optimize your next PCB project for cost, quality, and time-to-market needs.
What is PCB Assembly?
PCB assembly, also known as PCBA or PCB population, refers to the process of soldering and assembling electronic components onto a PCB or printed circuit board. It involves taking a bare PCB fabricated with copper traces connecting mounting pads and installing components like ICs, resistors, capacitors, connectors, etc., in designated locations on the board.
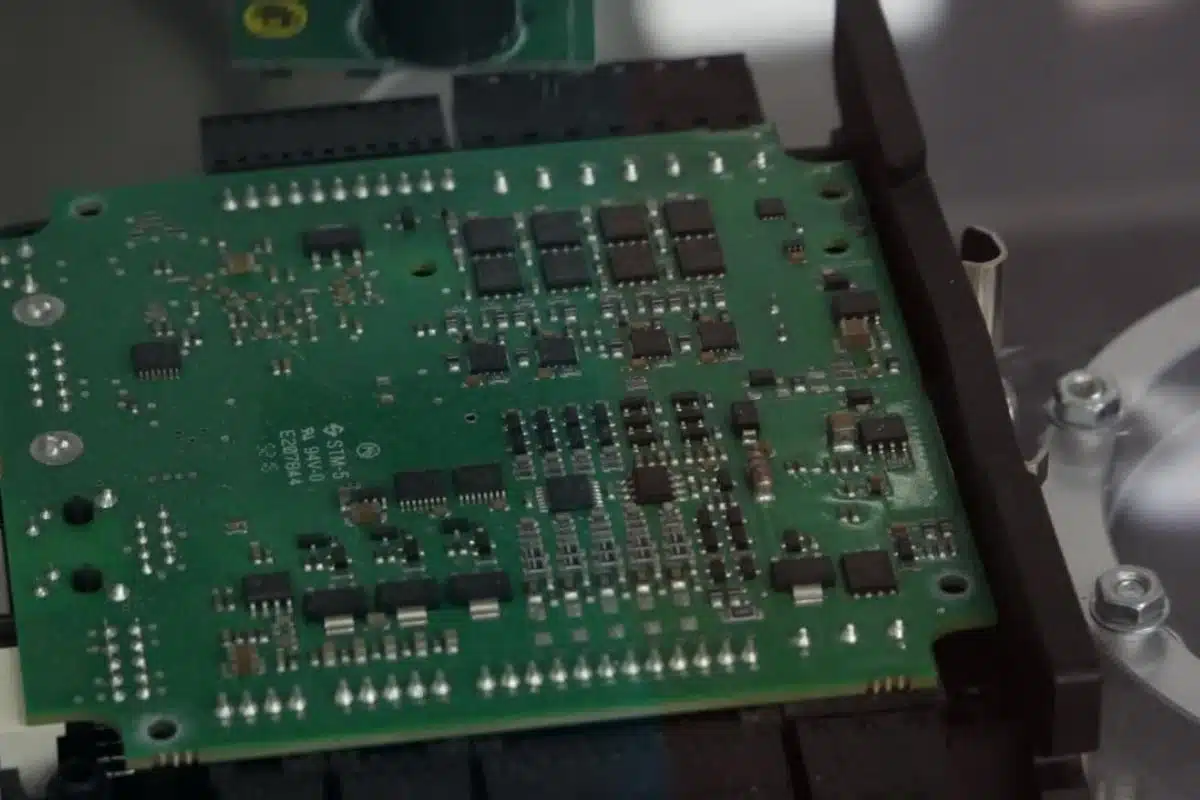

Working Principles of PCB Assembly
The working principles of PCB Assembly involve mounting electronic components onto the PCB, establishing electrical connections through conductive traces, and ensuring proper signal transmission. Adhering to these principles ensures the production of high-quality and reliable PCB assemblies essential for electronic devices to function properly.
1. Relationship Between Components and PCB
Electronic components such as resistors, capacitors, integrated circuits (ICs), and connectors are essential for any electronic device to function. These components are mounted onto a PCB using through-hole or surface mount technology.
In through-hole mounting, components are inserted into holes drilled into the PCB, and their leads are bent and soldered on the opposite side of the board. In SMT, components are fitted directly onto the surface of the PCB and held in place by solder paste.
2. Electrical Connections in PCB Assembly
The electrical connections between the components and the PCB are established through conductive tracks or traces on the PCB. These traces are made up of copper foil laminated onto the PCB substrate.
Components are mounted onto a PCB and connected to the conductive traces via leads or pads. The traces enable communication between the components, facilitating the flow of electricity and data within the circuit.
3. Signal Transmission in PCB Assembly
Signal transmission is an essential aspect of PCB assembly. It involves the transfer of analog and digital signals between different components on the PCB. This is achieved through signal traces that connect various input/output (I/O) ports and other components on the PCB.
Signal traces can be designed as single-ended, differential pairs, or controlled impedance. Single-ended traces are used for simple signals, while differential pairs are used for high-speed signals that require noise immunity. Controlled impedance traces are designed to maintain consistent signal quality across different frequencies.
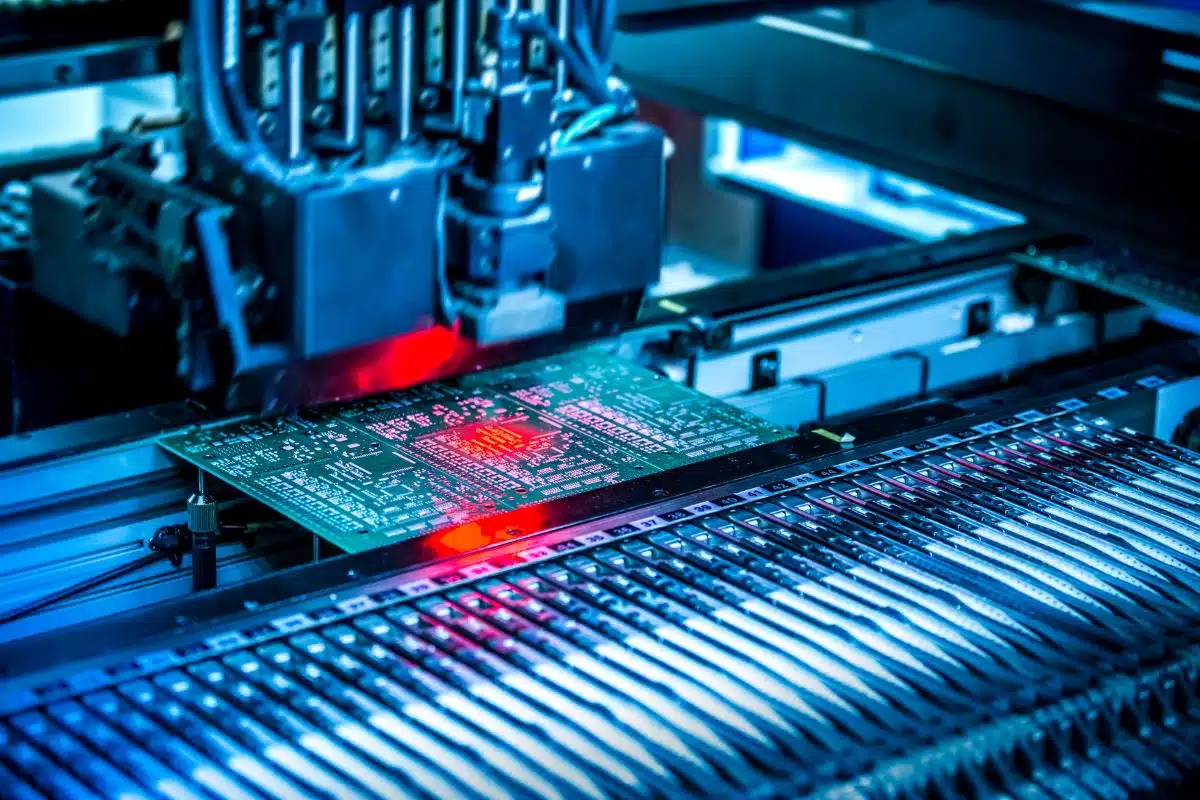
PCB Assembly Manufacturing Process
PCB assembly involves a series of steps that ensure electronic components are mounted, soldered, and tested properly to function together. Here are the main stages involved in the PCB assembly manufacturing process:
1. Design and Layout
The design and layout stage involves creating a schematic diagram that outlines the electrical connections between various components on the PCB. The layout is created using computer-aided design (CAD) software, which allows for precise placement of components and traces.
2. PCB Manufacturing
The PCB manufacturing process begins with choosing the right type of substrate material, such as fiberglass or ceramic, and then applying a layer of copper to the surface of the substrate. This copper layer is then etched away in the areas where it is not needed, leaving behind the desired pattern of conductive traces.
Once the PCB is manufactured, the next step is to procure the components required for the assembly. This involves sourcing components from authorized suppliers to ensure their quality, reliability, and compatibility with the PCB design.
A stencil is used to apply solder paste onto the pads on the PCB. The stencil is created using laser cutting technology, which ensures precision and consistency.
During component placement, the electronic components are mounted onto the PCB according to the design specifications. This can be done using through-hole or surface mount technology.
In SMT, the components are placed directly onto the surface of the PCB and held in place by solder paste. In through-hole mounting, components are inserted into holes drilled into the PCB, and their leads are bent and soldered on the opposite side of the board.
Reflow soldering is the process of melting the solder paste to establish electrical connections between the components and the PCB. The PCB is heated using an oven or a conveyor belt, ensuring the solder paste melts and flows onto the pads and component leads.
After soldering, the PCB assembly undergoes inspection and testing to ensure it functions properly. Various tests, such as visual inspection, automated optical inspection (AOI), and X-ray inspection are performed to detect any defects in the assembly, such as solder bridges, misaligned components, or cold joints.
Functional testing is also conducted to check if the PCB assembly performs the intended functions per the specifications.
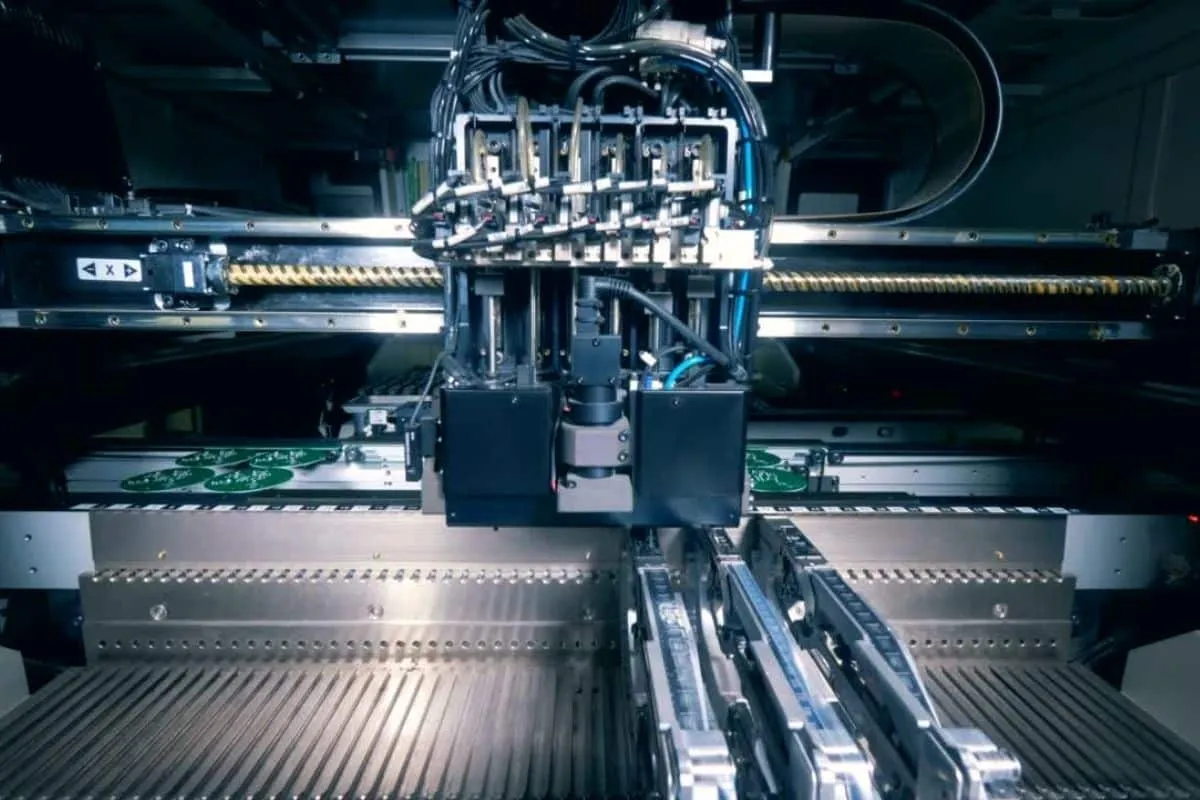
Key Terminology in PCB Assembly
PCB assembly involves many technical terms that are good to know. Here are definitions of some common PCB assembly terminology:
- Solder Paste – A mixture of solder particles and flux used for SMT soldering. It is applied on PCB pads by stencil printing.
- Pick and Place – The automated machine that uses vacuum nozzles to quickly and precisely pick and place components on a PCB.
- Solder Mask – A coated layer on the PCB that protects copper traces from solder and prevents shorts.
- Reflow Oven – A convection oven that heats SMDs on a PCB to melt solder paste and form solder joints.
- Through-Hole Components – Parts with wire leads that mount by inserting into holes in the PCB.
- Bill of Materials (BOM) – A list of all the components required to assemble a PCB.
- Gerber Files – Standard file format used for PCB fabrication data like copper layers, silkscreen, solder mask, etc.
- Fiducials – Alignment marks on a PCB allow automated machinery to orient the board precisely.
- Automated Optical Inspection – Imaging systems that scan assembled PCBs to detect defects.
- Boundary Scan – A test technique that allows testing of interconnects between components on a board.
- Flying Probe Test – Uses movable probes to test points on an assembled PCB electrically.
Knowing these key PCB terminology will help you better understand the assembly process specifications and communicate effectively with your contract assembler.
Frequently Asked Questions about PCB Assembly
PCB assembly is a complex process that involves several stages, and it can be challenging to address all the concerns related to it. Here are some frequently asked questions about PCB assembly:
1. What is the turnaround time for PCB assembly?
The turnaround time for PCB assembly depends on various factors such as the complexity of the design, the number of components, and the type of assembly service provider. Typically, the turnaround time can range from a few days to several weeks.
Learn more about our quick turn PCB assembly service
2. Do I need to provide my components for PCB assembly?
You can either provide your components or purchase them from your PCB assembly service provider. It is recommended to source components from authorized suppliers to ensure their quality and compatibility with the PCB design.
Learn more about our turnkey PCB assembly service and Consigned PCB assembly service.
3. How do you ensure quality in PCB assembly?
Stringent quality control through process controls, inspection at each step, testing of boards, and rigorous operator training is needed to achieve high assembly quality and long term reliability.
4. What are the advantages and disadvantages of through-hole and surface mount technology?
Through-hole technology is better suited for larger components or components that require higher mechanical strength, while surface mount technology is more suitable for smaller components or where space is limited. Through-hole technology can add extra cost and time to the PCB assembly process, whereas surface mount technology allows for a more compact design and faster manufacturing.
5. Can I rework or repair a PCB assembly?
Yes, it is possible to rework or repair a PCB assembly. However, this can be challenging because the rework process can affect the quality and reliability of the assembly. Working with an experienced PCB assembly service provider who can perform rework or repair effectively is recommended.
6. How are components attached to the PCB?
Most components are soldered to the PCB through wave, reflow, or manual soldering. Solder forms mechanical and electrical connections between component leads/pads and copper pads on the board.
7. What is the difference between through-hole and SMT components?
Through-hole components have long leads that go through holes in the PCB for soldering. SMT or surface mount components directly solder onto surface pads without leads going through holes.
8. How many components can be assembled on a PCB?
Anything from a few components to thousands of components can be assembled on a single PCB. Complexity depends on board size, layer count, and component density.
9. What data do I need to provide to a PCB assembler?
You will need Gerber files for PCB fabrication, bill of materials listing all components, assembly drawings, and any special instructions.
10. What are common PCB assembly errors?
Common errors include missing components, wrong components, bent leads, insufficient solder, shorts, open joints, misaligned components, etc.
11. What testing is done on assembled PCBs?
Testing includes in-circuit tests to validate functionality, flying probe tests to check shorts/opens, boundary scans for interconnects, and environmental stress tests for reliability.
PCB Assembly Industry Standards
To ensure quality and reliability, PCB assembly is governed by several industry standards. Understanding these standards can help you evaluate and select an assembly partner. Some of the main standards include:
IPC Standards
The IPC, or Association Connecting Electronics Industries, publishes numerous PCB standards. Some key ones are:
- IPC-A-610 – Acceptability standard for electronics assemblies. It specifies requirements for soldering, part placement, markings, and more.
- IPC J-STD-001 – Standard for soldering electronics assemblies. Covers materials, methods, inspection, etc.
- IPC-A-600 – Acceptability standard for printed boards. Includes fabrication quality requirements.
ISO Standards
Many ISO quality management standards apply to PCB assembly like:
- ISO 9001 – Sets requirements for quality management systems. Focuses on customer satisfaction, continuous improvement, and process control.
- ISO 13485 – Tailored for medical devices. Stringent QMS requirements for safety and effectiveness.
Environmental Standards
With rising environmental concerns, PCB assembly must comply with standards like:
- RoHS – Restricts use of hazardous substances like lead, mercury, and cadmium.
- WEEE – Mandates recycling and recovery programs for electronic waste.
- REACH – Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals.
Choosing an assembly partner certified in these standards ensures your PCB products meet quality and environmental requirements.
Choosing A PCB Assembly Partner
Choosing the right PCB assembly partner is critical for delivering quality boards on time. Here are some tips for selecting an EMS provider:
Evaluate Capabilities
- What assembly technologies do they have? Manual, SMT, advanced automation?
- Can they handle your board complexity and component types?
- Do they have in-house testing? This avoids delays waiting for 3rd party testing.
- Are they familiar with your industry’s standards? e.g., automotive, medical, etc.
Ask Questions
- What are their quality processes and controls? Inspect solder joints, test coverage, defect rates, etc.
- How do they ensure consistent product quality? Process audits, operator training, etc.
- Can they provide certifications for standards compliance e.g., ISO, IPC, RoHS?
- What are their lead times? Rushed assembly can lead to mistakes.
Evaluate Costs
- Get detailed quotations – material costs, assembly charges, test charges, etc.
- Compare pricing between vendors. Go for the best value, not just the lowest cost.
- Consider total cost, not just unit price. Factors like minimum order quantities, tooling charges, and handling fees impact overall cost.
Do Due Diligence
- Check reviews and references. Visit their facility if possible.
- Review their component inventory. Wider selection reduces procurement delays.
- Ensure they have strong supply chain partnerships. This prevents component shortages.
- Evaluate their financials and manufacturing capacity. Ensure they can support your production needs.
Evaluating potential assembly partners thoroughly will help prevent issues and result in a smoother PCB production process.
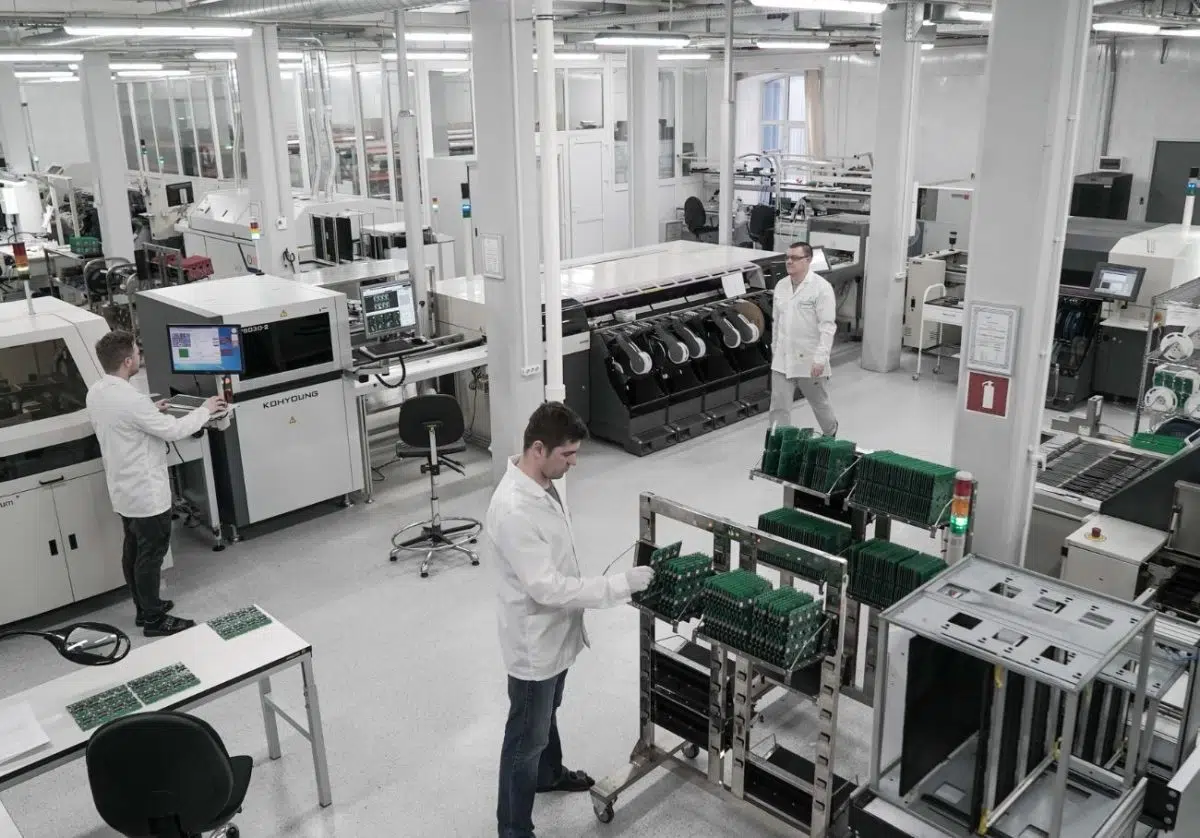

Leading PCB Assembly Manufacturer in China
If you are looking for a professional and reliable PCB assembly manufacturer, look no further than our company. We have years of experience in the industry and adhere to the highest standards of quality and reliability.
Our team of experts is committed to providing you with the best PCB assembly services, from design and layout to component procurement, stencil production, component placement, reflow soldering, inspection, and testing. We also comply with industry standards such as IPC, ISO, RoHS, and UL certification to ensure that your electronic devices meet regulatory compliance requirements.
Contact us today to learn how we can help you with your PCB assembly needs. Our team is ready to answer any questions and provide a customized solution that meets your requirements. Let us help you create high-quality and reliable PCB assemblies for your electronic devices.





















