PCB Manufacturing Services
Rigid PCB Board
The Rise of Rigid PCBs
Due to the development trend of aerospace products, including lightweight, miniaturization, multifunction, and assembly densification, a higher requirement has been founded for printed circuit board (PCB) technology and manufacturing process. Rigid PCBs are a kind of circuit board that is fabricated from different substrate materials and have more advantages than ordinarily PCBs.
Furthermore, electromagnetic signals can run quickly and smoothly in rigid PCBs due to the excellent electrical performance and thermal performance of rigid substrate material so rigid PCBs are widely applied in many industries like instruments, automotive, treatment, military, and aerospace. Based on the further development and optimization of rigid PCBs, the subsequent step for them should be Rigid PCBs, Embedded Rigid Circuits, and HDI Flex PCBs, among which Rigid PCBs attracts the foremost attention and applications.
Rigid PCB Definition
What is Rigid PCB?
A rigid PCB is a Solid, inflexible printed circuit Board. We all know that a PCB is Single Sided PCB, Double Sided PCB, or Multilayer PCB. At the identical time, a printed circuit board is often Rigid, Flexible, or Rigid-Flex (A combination of Rigid and versatile PCB). So, a Rigid board is a Board that we cannot bend or force out of shape. It’s not flexible. A Rigid PCB can be Single Sided, Double Sided, or Multilayer board.
Once a Rigid printed circuit is manufactured it cannot be modified or folded into the other shape. A rigid circuit card is created of the solid substrate with copper tracks and component layouts where Active and Passive Electronic Components (Through-Hole, SMD Components, or Mixed PCB Assembly) are soldered either by automated Through Hole Soldering Technology like Wave Soldering or Automated Surface Mount Technology (SMT) like Reflow Soldering and Hand Soldering can also be done.
Characteristics of Rigid PCB
Here are some characteristics of Rigid PCB:
- Rigid PCB is a quite conventional PCB, which may not be like Flexi PCB because rigid PCB cannot be twisted or folded into any shape because it’s FR4 reinforcement, which is incredibly useful for increasing stiffness.
- Rigid PCB comprises copper trances and paths, which are incorporated on one board to attach the various components. The bottom material of the board is created of a rigid substrate which provides rigidity and strength to the board.
- The computer motherboard is the best example of a rigid PCB with a rigid substrate material.
- Once rigid PCBs are manufactured, they cannot be modified or folded into the other shape.
- Rigid PCB is cheaper than flexible PCB. They’re traditional PCBs and are widely utilized in many electronic products.
- Flexible PCB and rigid PCB have their limitations and advantages in terms of easy use and availability. Both of them are wont to connect multiple electronic components on circuit boards.
How to make a rigid PCB?
Like any other PCB, rigid PCBs are manufactured by following a certain process. Here, we will discuss each phase in the whole manufacturing process of a Rigid printed circuit board.

Rigid PCB Manufacturing Process
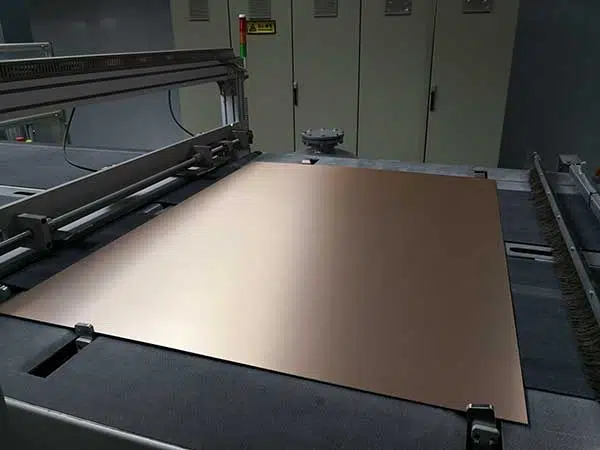
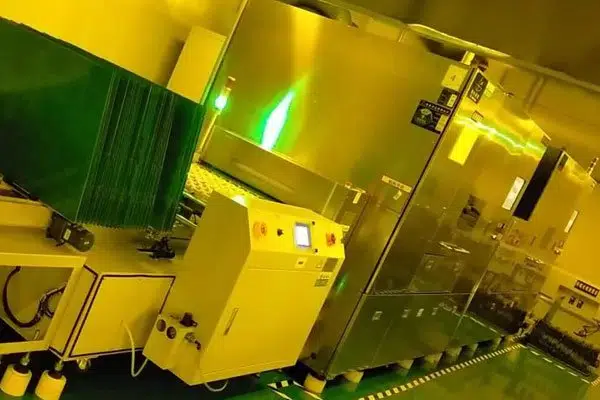
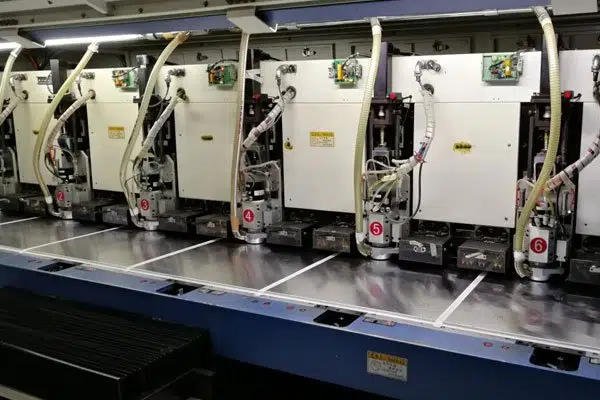







These are the fundamental steps utilized in the assembly of rigid PCBs. These PCBs are often constructed with single, double, and multiple layers. For a PCB to satisfy all requirements of the application, it’s important to produce detailed information about the appliance to the PCB manufacturer. This can allow him to style the PCB in step with your needs.
Rigid PCB Stack
Layers of Rigid PCB Board
Rigid PCB contains different layers that are joined together using adhesive and warmness, providing a stable form to board material. Following layers are used to develop a rigid PCB.
Substrate Layer
The substrate layer, also referred base material, is formed of fiberglass. The FR4 is especially used as a substrate material, the foremost common fiberglass that has rigidity and stiffness to the board. Phenolics and epoxies are used as a base material, but they're not pretty much as good as FR4. However, they're less costly and have a novel lousy smell. The decomposition temperature of phenolics is simply too low, leading to delamination of the layer if solder is placed for an extended time.
Copper Layer
On the highest of the substrate layer, a copper foil is laminated on the board with the assistance of the added amount of warmth and adhesive. In everyday use, each side of the board is laminated with copper; however, some cheap electronics include just one layer of copper material on the board. Different boards include different thicknesses, which are described in ounces per sq ft.
Solder Mask Layer
Solder Mask Layer houses above the copper layer. This layer is added to the board to feature insulation on the copper layer to avoid any damage if any conduction material is touched by the copper layer.
Silkscreen Layer
The silkscreen layer is found above the solder mask layer. It's wont to add characters or symbols on the board to grasp the board better. White color is especially used for silkscreen. However, other colors also are available, including grey, red, black, and yellow.
Benefits of Rigid PCB
- More affordable as compared to flexible PCB.
- long-lasting than flexible Circuit Boards.
- High quality and density.
- Widely used in numerous electronic devices.
- More market and supply.
Uses of Rigid PCB
Rigid printed circuit boards offer increased circuit density and might reduce the size and overall weight of the board. This is why JHYPCB use these boards in their several electronic devices and gadgets:
- Computers and Laptops
- Telecommunications Equipment – transportable, Tablets and other Hand Help Devices
- File server and Data storage
- Signal transmission, mobile repeaters, GPS
- Satellite
- Medical Equipment: Testing, X-Ray, cardiac monitor, CAT Scan
- Industrial Equipment
- Atomic and Nuclear Systems
- Military and Defense Equipment
- Automotive
- Aerospace
Anywhere, where complex Circuitry is required


Rigid PCB Manufacturing Capabilities
- Up to 64 Layers
- IPC Class 2|PC Class 3
- Max Board Size: 609 * 889 mm
- Board Thickness: 0.1~8.0mm
- Max finished copper thickness: 6 OZ
- Min Laser Drilling Hole Size: 3mil(0.075mm)
- Min CNC Drilling Hole Size: 0.15mm
FAQs
Rigid PCB can be divided into single-sided rigid PCB, double-sided rigid PCB, and multi-layer rigid PCB according to the number of layers.
Well-known PCB design software (computer-aided design, CAD) includes OrCAD, Pads (PowerPCB), Altium Designer, FreePCB, CAM350, etc.
Absolutely. We can provide flexible PCB manufacturing services for up to 10 layers.
Learn more about our flexible PCB capabilities.
Both rigid and flexible PCBs have their own advantages. The choice of rigid or flexible PCB depends on cost and application needs.
Materials used to manufacture printed circuit boards must have good heat dissipation and insulation properties. A commonly used rigid PCB material is FR-4. JHYPCB provides FR-4, High Tg, Shengyi, Rogers, Arlon, Halogen Free, IT180, Isola, etc.












